| Cardiac | |
|---|---|
| GI | |
| Bone | |
| GU | |
| Neuro | |
| Faculty | |
| Student | |
| Quizzes | |
| Image DDX | |
| Misc |
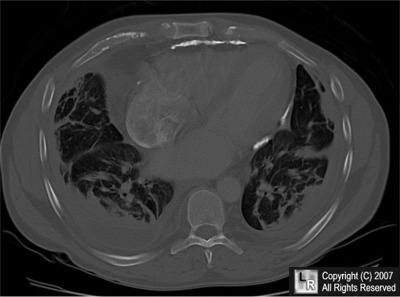
What's the most likely diagnosis?
- 47 year-old with dyspnea
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy
- Constrictive pericarditis
- Asbestos-related pleural disease
- Sarcoidosis
- Mesothelioma
![]()
Answer:
2. Constrictive pericarditis
More (Click Discussion Tab)
Constrictive pericarditis
General considerations
- Defined by thickening of pericardium (>4mm) impeding diastolic filling
- Thickened pericardium may calcify (50%)
- Calcified pericardium almost always implies constriction, but not always
- About 50% of calcified pericardiums are visible on conventional radiography
- Calcification of the pericardium is most likely inflammatory in nature
- Can be seen with a variety of infections, trauma, and neoplasms
- Most common causes include
- Viral pericarditis (most common)
- Tuberculous pericarditis
- Uremic pericarditis
- Post-cardiac surgery
- Calcification most commonly occurs along the inferior diaphragmatic surface of the pericardium surrounding the ventricles
- Thin, egg-shell like calcification is more often associated with viral infection or uremia
- Calcification from old TB is often thick, confluent, and irregular in appearance, especially when compared with myocardial calcification
|
LearningRadiology.com is an award-winning educational site aimed primarily at medical students and radiology residents-in-training, containing lectures, handouts, images, Cases of the Week, archives of case quizzes, flashcards of differential diagnoses and “most commons” lists, primarily in the areas of chest, GI, cardiac, and bone radiology.